Overview
Users can add or remove networks without having to carry out extensive configuration themselves.
The following products are available to users:
Virtual Network: Virtual networks are made up of virtual network links.
Firewall: A firewall is used to protect the network from undesirable network-traffic.
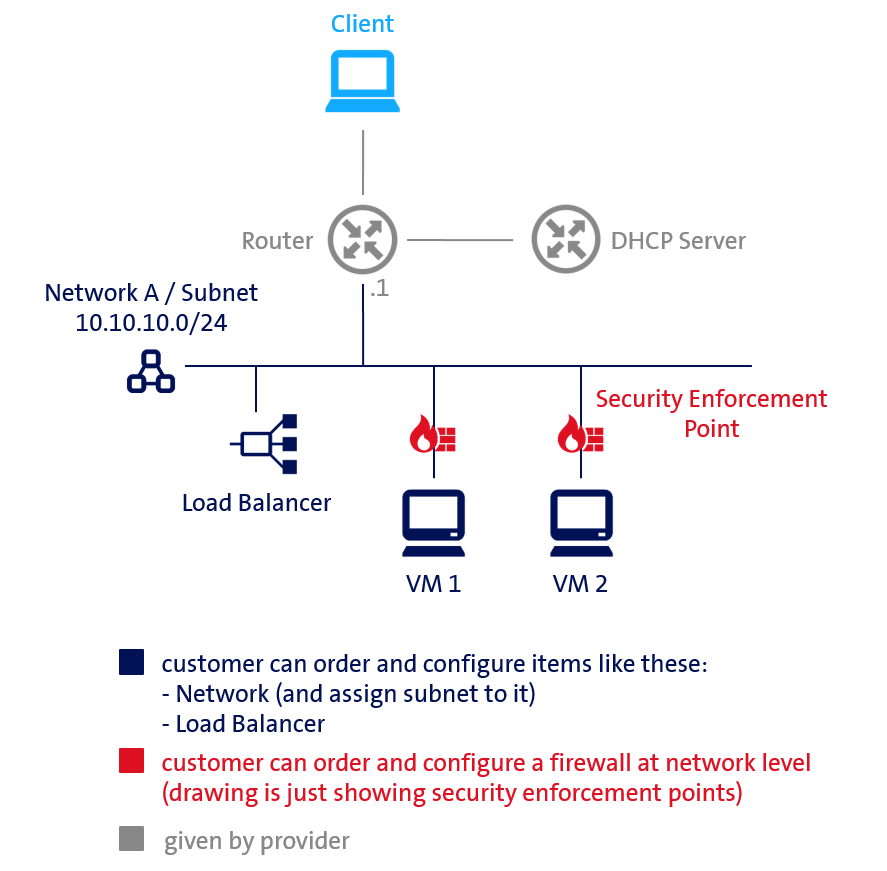
The customer orders a network with X IP addresses. The first IP address is needed for the router, which is provided by the provider. As long as there are available IP addresses it is possible to attach a load balancer and VMs to the network.
A load balancer always needs one IP address. Additionally, it is necessary to create at least one Virtual Server. A Virtual Server needs one IP address, but this IP address could be shared with other Virtual Servers on the same load balancer.
For every VM which is assigned to the network an IP address is needed.
Virtual Network functionalities
Switching
ESC provides complete mapping of the switching functionality in a virtual environment, irrespective of the underlying hardware. The logical switch is a distributed basic component to make a Virtual Machine available. The separation of the networks is ensured by VXLAN.
When setting up a network you can choose between a routed and an isolated network. Most networks are usually routed networks connected directly to the distributed router. Isolated networks are completely shut off and are used, for example, for the heartbeat connection of a DB cluster.
Routing
Within an isolated network environment (definition depending upon design) the various routed networks communicate via the distributed routers. The individual networks are dynamically published to the uplink routers.
The virtual environment is connected with the outside world via the virtual uplink routers (e.g. client network).
Several routers are operated in parallel with ECMP (equal cost multi path) as the uplink router to ensure bandwidth scalability. A minimum of 2 and maximum of 8 routers are available. The provision/upgrading of the uplink router is not carried out via self-service. The transition to the physical network requires routers that support ECMP and BGP.
IP Address Management
The IPAM solution of the Enterprise Service Cloud includes the management of IPs and DHCP. This also comprises the tracking of all used and free IP addresses and the creation of sub-networks.
The IP addresses (IPv4) are managed in the basic product. They define an area to be used for your virtual environment. When creating new networks, sub-networks can be obtained from the pre-defined area.
When assigning the IP addresses of an individual network you can choose between static and dynamic allocation and configure the DNS settings (primary & secondary name servers and DNS suffix).
The IP address management and the IP range management are carried out in the inventory. The IP pools are stored in the inventory which serves as an IP address pool.
DNS
The workloads of Virtual Machines are configured with the associated DNS settings (primary, secondary name servers and DNS suffix). The basic product of the Enterprise Service Cloud does not include pushing to a DNS server or the configuration of DNS servers.
